Cheap SSL Certificates
Single Domain SSL Certificates
Secure a single website with strong 256-bit encryption to protect data and improve Google rankings. Buy our single domain SSL certificates at the cheapest prices.
Multi Domain SSL Certificates
Enable industry-standard encryption across your all different websites using a single multi-domain (SAN) SSL certificate to reduce administrative hassle.
Wildcard SSL Certificates
Secure your primary website and its unlimited sub-domains including the mail server by requesting a one wildcard SSL certificate with an asterisk (*.domain.com).
Code Signing Certificates
Get a digital signature to your software and application code with our code signing certificates to make it more legit. It will help you to increase downloads.
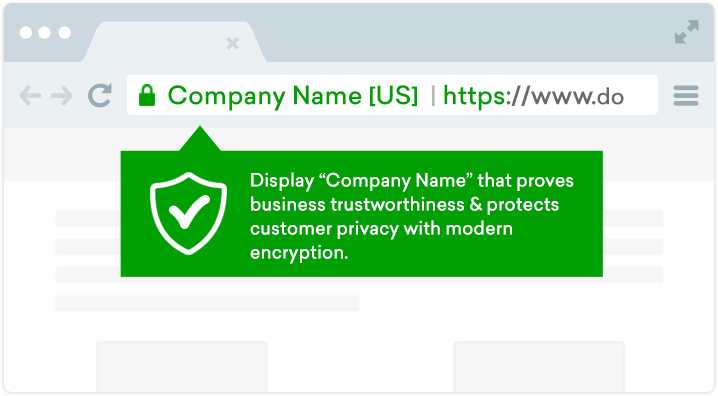
EV SSL Certificates
EV SSL certificates bring the highest level of protection to a site, prove business reliability and enhance trust by displaying “Company Name” under secure padlock icon.
Benefits of SSL/HTTPS Certificate
Bring easy certificate management to your fingertips and robust encryption at a discounted price.
Increase Customer Trust
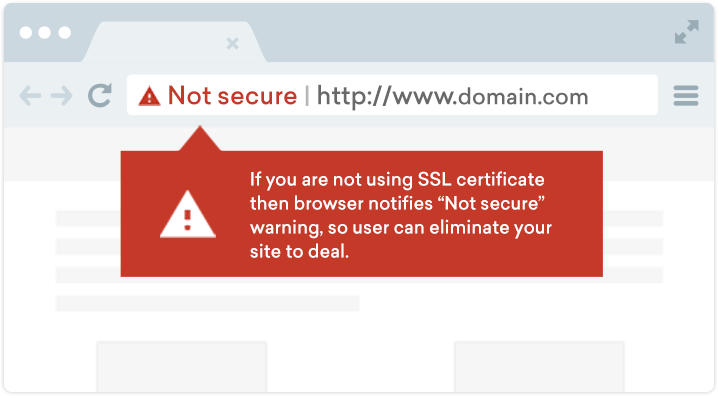
Say ‘No’ to Insecure Warning
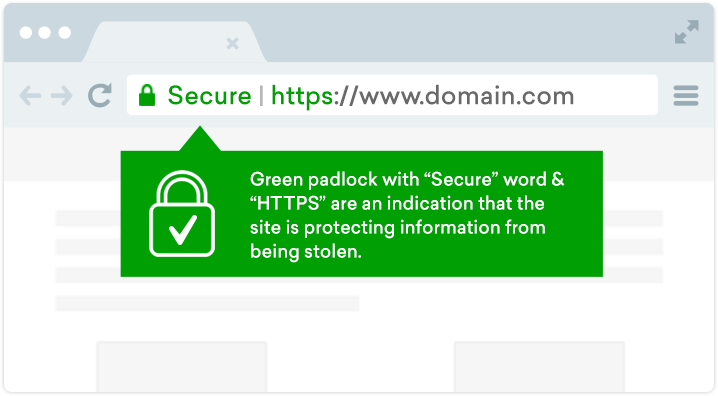
Protect Customer Data
SSL Site Seal
SEO Rank Boost
Browser Ubiquity
Google  Security
Security
to get your products or services with confidence.
Why To Buy SSL Certificates from ClickSSL?
ClickSSL is the best cheap SSL certificate provider that offers robust encryption with each SSL security. From reputed SSL brands, you will get many features and advantages that you may hardly get from others. Whether you go with a single domain, a multi-domain, or wildcard SSL, you will get a handsome discount on your every purchase. Easy sign-up, quick renewal, and other useful features, along with 24/7 technical support, give us a great stance among rivals.
How to Purchase SSL Certificate?
1. Select Your SSL Certificate
Browse through the various SSL certificate options available on the ClickSSL website. You can choose from a range of certificates such as DV SSL, OV SSL, EV SSL, Multi-domain and Wildcard SSL certificates. After making your choice, click “Buy Now.”
2. Review and Checkout
Review your shopping cart and make any changes at this stage. Click on “Proceed to Checkout” to initiate the checkout process. If you’re a new customer, you’ll be asked to create an account. Existing customers can simply log in. Provide billing information such as your name, address, and payment details. You can pay using the mode of payment of your choice.
3. Configure SSL
Once your order is confirmed, you’ll receive an email with instructions to configure the SSL certificate. Follow the steps to install it on your server. After completing the configuration, the certificate authority will validate your information and issue the SSL certificate.
Worldwide Best SSL Certificate Provider
discounts on our SSL products. Purchase SSL certificate today!
SSL Reseller & Partner Program
ClickSSL has brought an innovative and profitable reseller program for IT businesses and entrepreneurs who are eager to start their own SSL business or expand their current product range by adding SSL certificates. Take the advantage of full-featured API and cPanel along with a free web store that allows selling SSL with your own brand by setting up your own profit margin. Do peaceful business with us without worrying about deadlines and unimaginable targets.