What is a Certificate Authority? What does CA stand for? Why are CAs so crucial in the internet world? What do CAs do? All answers and explanations to these questions will be provided in this article. But before we delve further into the definition of a certificate authority, let me pause for a second and ask you something. How likely are you to hand over your sensitive information or banking information to a stranger on the street? I heard you clearly- You cannot do such a thing.
It will surprise you to learn that people often do the digital equivalent of that when they exchange such information with websites. For instance, website visitors will enter their personal information on eCommerce websites, and exchange their banking details, credit card numbers, and social security numbers, among many other pieces of sensitive data. What is more alarming is that web users often do not know whether the websites are secure or trustworthy.
Before providing your sensitive information, you should ask yourself: how can you establish whether a website is trustworthy? And how can you know that you are transmitting your data securely? This is where the idea of a certificate authority comes into view. This article has addressed top issues of certificate authorities that people often seek to find out. So let us start by understanding what certificate authority is.
What is Certificate Authority?
Certificate Authority or SSL certification authorities refer to a trusted third-party entity primarily concerned with verifying and validating websites, email addresses, entities and individual persons and binding them to cryptographic keys by issuing digital certificates. Thus, a digital certificate ensures data integrity and encryption and identity validation. As you can see, certificate authorities play a pivotal role in digital security.
Certificate Authority is Like Internet Passport Authorities
Traveling internationally requires a passport that validates your identity to someone who hasn’t met you before. After a thorough vetting system, when you finally receive your passport, you can be assured of smooth and secure international transit without worrying about anyone questioning your identity.
Taking this analogy to the cyber world, the task of vetting and issuing digital certificates to organizations’ websites is done by bodies named Certificate Authorities. They verify your organization’s existence or domain’s ownership and issue digital certificates after the process is complete.
This digital certificate serves the same purpose as a passport in the physical world. To understand the workings of a CA in detail, read on.
How Certificate Authority Works? The Technical Nitty-Gritty
Certificate Authorities are the cogs in the wheel of an umbrella term called Public Key Infrastructure technology, commonly abbreviated as PKI.
Let’s get started with how Cas or the certification authority works with securing website connections. Whenever you spot a secure padlock symbol at the beginning of an URL in the address bar, you know for sure that the connection is HTTPS enabled. The protocol that enables the same goes by the name of SSL or, more correctly, TLS certificates.
SSL or Secure Socket Layer certs employ PKI and need the following prerequisites to function smoothly.
- Digital Certificate: CA certificate is a symbol of trust and security that bears testimony to the website’s identity.
- Certificate Authority: Certificate authority is a renowned organization that is responsible for verifying the website and issuing the certificate.
- Digital Signature: This shows that a reliable CA issued the SSL/TLS certificate.
- Public Key: Employed by the browser to encrypt the data communicated to the site.
- Private Key: Employed by the website to decrypt the data transmitted to it.
What Does a Certificate Authority Do?
1. The Verification Role
The primary reason why certificate authorities exist is to play the verification role. I will explain to you how this works.
First, a website will approach a certificate authority to request a digital certificate. The certificate authority does not give out the certificate immediately. It will first have to verify the website’s validity depending on the certificate type the website requests. There are three validation levels, as explained below;
Domain Validation
With domain validation, the CA will only need to establish whether the requestor is the legitimate owner of the website or domain. This validation level usually takes little time. Moreover, it is the bare minimum level of validation that one will have to go through.
Organization Validation
Apart from confirming the identity and legitimacy of the requestor, the certificate authority goes a notch higher to perform basic business validation. The organization validation process usually involves a human element. The CA will do thorough research, perusing third-party records sources to ensure that certificate requestors are what they say.
Extended Validation
Extended validation is the top validation level. Because of the technicalities involved, the requestor takes quite some time to receive the certificate under this validation level. The certificates will take up to five days before they are issued. In addition, the CA will take extensive research into an organization to ensure that the organization is indeed legitimate.
Recommended: DV SSL vs OV SSL vs EV SSL Certificate – Differences Explained
2. List of Trusted Certificate Authorites
Devices and browsers trust several Certificate Authorities. One factor to be considered is the number of years in operation. While the certificates are compatible with almost 99% of browsers, it is better if they are backward compatible too. We will provide an overview of some of the trusted ones here.
#1. DigiCert
DigiCert is a renowned brand in PKI, SSL and IoT solutions and was founded in 2003. They had also won the Frost & Sullivan Global TLS Certificate Company of the Year in 2020.
The brand offers SSL certificates with the latest technology and supports 2048-bit public key encryption (3072-bit and 4096-bit are available too). The products also support the RSA public-key SHA-2 algorithm and ECC public-key cryptography.
#2. RapidSSL
A subsidiary of GeoTrust Inc, RapidSSL is a trusted Certificate Authority that came into existence in the year 2003. Renowned for low-cost and fast issuance of standard and wildcard SSL certificates, it is endowed with the latest encryption standards and modern infrastructure.
It offers 256-bit encryption and 99.9% browser compatibility. The perfect choice for your brand is a well-respected symbol of trust.
#3. GeoTrust
GeoTrust was the pioneer CA to initiate domain-validated certificates which today dominate cyberspace. Bought by Symantec from Verisign in the year 2010, it has lived up to its pioneering status.
It offers unbeatable 256-bit encryption, SHA2 and ECC support, and free unlimited re-issuance during the certificate lifespan amongst other benefits. Its low-cost SSL options are a boon for business owners who seek to strengthen their security and improve SERP rankings.
#4. Thawte
Established in the year 1995, in South Africa, it has now spread roots globally and has issued 945,000+ certificates. It gives you a whole host of benefits which include, unlimited server licenses, free Thawte trusted site seal, complete business authentication and more at unbelievably low prices!
#5. Comodo
Comodo provides internet security solutions that freelancers can use for their blog sites and e-commerce brands alike. The products offer 256-bit encryption, licenses for unlimited servers and comprehensive customer support.
The brand is also recognized for its world-class client support and innovative products.
The brand provides an entire range of TLS certificates and has provided over 100 million such certificates.
3. A Certificate Authority’s Role in the Chain of Trust
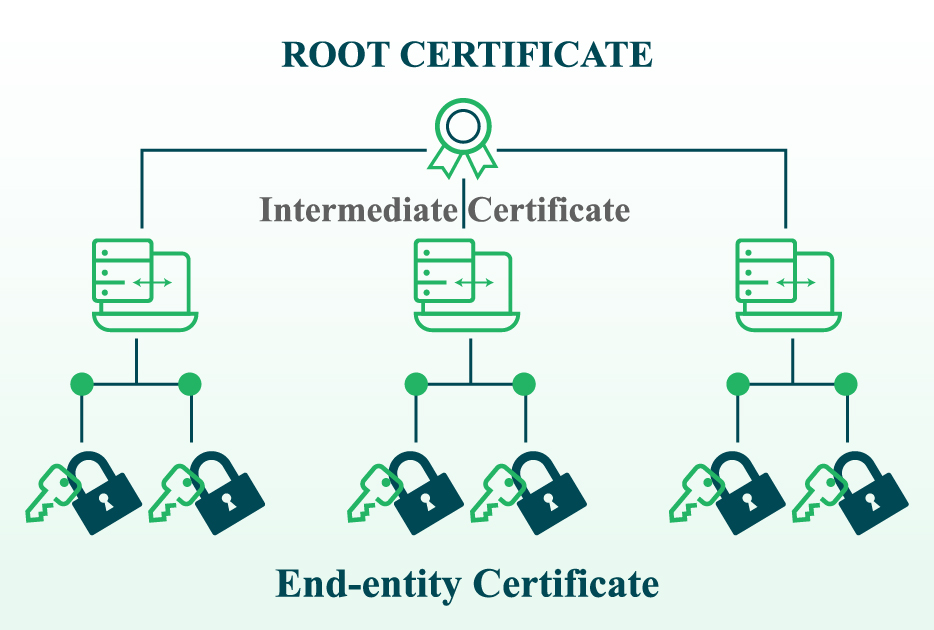
Digital certificates are based on a trust relationship model referred to as the certificate chain of trust. The chain of trust comprises a series of certificates that all link to the certificate authority. Basically, the trust model that all certificate authorities apply comprises root certificates, intermediate certificates, and server or end-entity certificates, as shown in the figure below.
Now, think of the certificate chain of trust as an upside-down tree. The root certificates are like the pillars or roots that hold the whole process together. The intermediate certificates are the stem, and the end-entity certificates are the leaves with a limited life span.
To understand this more, let us look at the individual elements on the certificate chain of trust.
A Root Certificate
The root certificate is the one signed and issued by the certificate authority. As you realize, the CAs will pay a close eye on the certificates to ensure they are safe. Operating systems and web browsers contain a list of trusted root certificates.
An Intermediate Certificate
Root certificates issue intermediate certificates. See where this is going? A root certificate authority delegates its authority to issue digital certificates to intermediate certificate authorities. In short, intermediate certificates act as the ‘intermediary’ between root certificates and server certificates. Suppose a hacker compromises an intermediate certificate; only server certificates will be affected, not the root certificates.
Also Read: Root Certificates vs Intermediate Certificates
End-entity Certificates
Also referred to as end-entity certificates or leaf certificates, the certificate authority will issue the server certificate for your website or domain. They usually have a limited lifespan of about 398 days.
4. The role played by CAs in Certificate Revocation
The role of certificate revocation lies in the hands of the certificate authority.
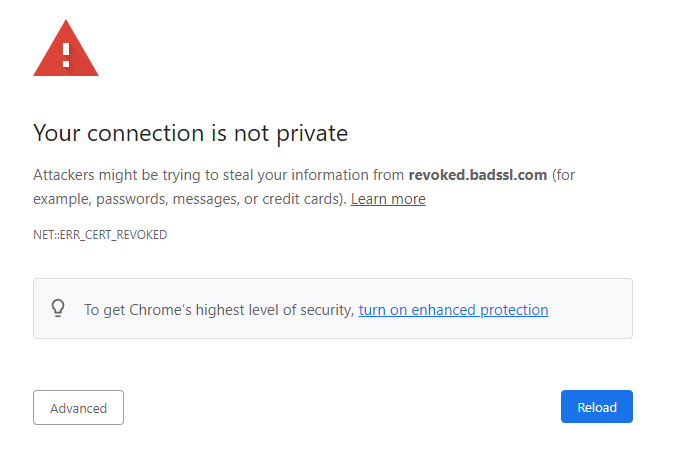
As the name suggests, certificate revocation refers to the process of filtering valid from invalid certificates. Basically, a certificate authority will want to make it known that one or more of its certificates have been compromised and should not be trusted in any way whatsoever.
Should a certificate authority revoke a certificate on your website or domain, it will prompt web browsers to display a warning message “Your connection is not private” which is shown in the image below;
The Difference Between Public Certificate Authority and a Private CA
Public and private certificate authorities are the most critical players in the game of digital certificates. Most of the newbies in the game usually do not know the distinction between the two. And yes, understanding the differences is so important.
Although the terms look quite self-explanatory, I will go ahead and briefly break down the distinctions so that everyone understands what they mean.
A public certificate authority refers to a third-party organization concerned with issuing certificates at a fee upon doing the necessary validation on the organization requesting the certificate.
Also known as the private, public key infrastructure, the private certificate authority is an internal certificate authority existing within a larger organization or enterprise and which has the powers to issue its certificates. Look at a private CA as a local CA created by an organization without necessarily going for the external one. In this scenario, the certificates are signed by the root certificates of the enterprise.
Whereas a private CA operates in the same manner as its public counterparts, the most conspicuous distinctions that you must note are;
- The certificates of a private CA are only trusted by the internal users
- The use of certificates issued by a private CA are restricted to a select group of users or clients
- The role of setting up and hosting the certificates offered by the private certificate authorities.
Who Decides Which Certificate Authorities Are Publicly Trusted?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer on who decides which certificate authorities are publicly trusted. For instance:
- Microsoft will determine the certificate authorities trusted by windows devices
- Mozilla will determine the certificate authorities to be trusted by Linux and Firefox devices
- Apple will decide the certificate authorities to be trusted by safari browsers and operating systems from Apple.
Conclusion of Certificate Authority
The internet is a vulnerable place, and there is no single doubt about that. The alarming rate of cyber breaches and the increasing costs of data breaches should make you think twice about surfing the internet. But you do not have to worry if you know the effective cybersecurity tips that will make you secure. For instance, you need a trusted third party to bring identity and trust to your table.
The primary reason for certificate authorities is to bring security to the internet and make it a secure place for entities and users. This article has explained what does certificate means, the workings of the CAs, among other technical nitty-gritty of certificate authorities.